Getting a good night’s sleep is essential for our overall health and well-being.
Sleep plays a crucial role in physical and mental restoration, allowing our bodies to repair and recharge for the next day. A lack of sleep, on the other hand, can have a significant impact on our health, including fatigue, irritability, and increased risk of serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
In this article, we’ll discuss the different stages of sleep, the effects of sleep deprivation, and tips for better sleep. By understanding the importance of sleep and how to improve it, you’ll be on your way to getting the sweet dreams your body needs to feel refreshed and rejuvenated.
The Different Stages of Sleep
During non-REM sleep, which makes up the majority of our sleep, our bodies go through several stages of increasing and decreasing muscle tone and brain activity. The first stage of non-REM sleep is called N1 and is considered the lightest stage of sleep. During N2, our bodies continue to relax, and our brain activity slows down even more. The third stage of non-REM sleep, N3, is considered the deepest stage of sleep and is when our bodies repair and restore themselves.
REM sleep is the stage of sleep when we have vivid dreams. During this stage, our brain activity is high, and our bodies are temporarily paralyzed. This stage is critical for our mental restoration, allowing our brains to process and consolidate memories and emotions.
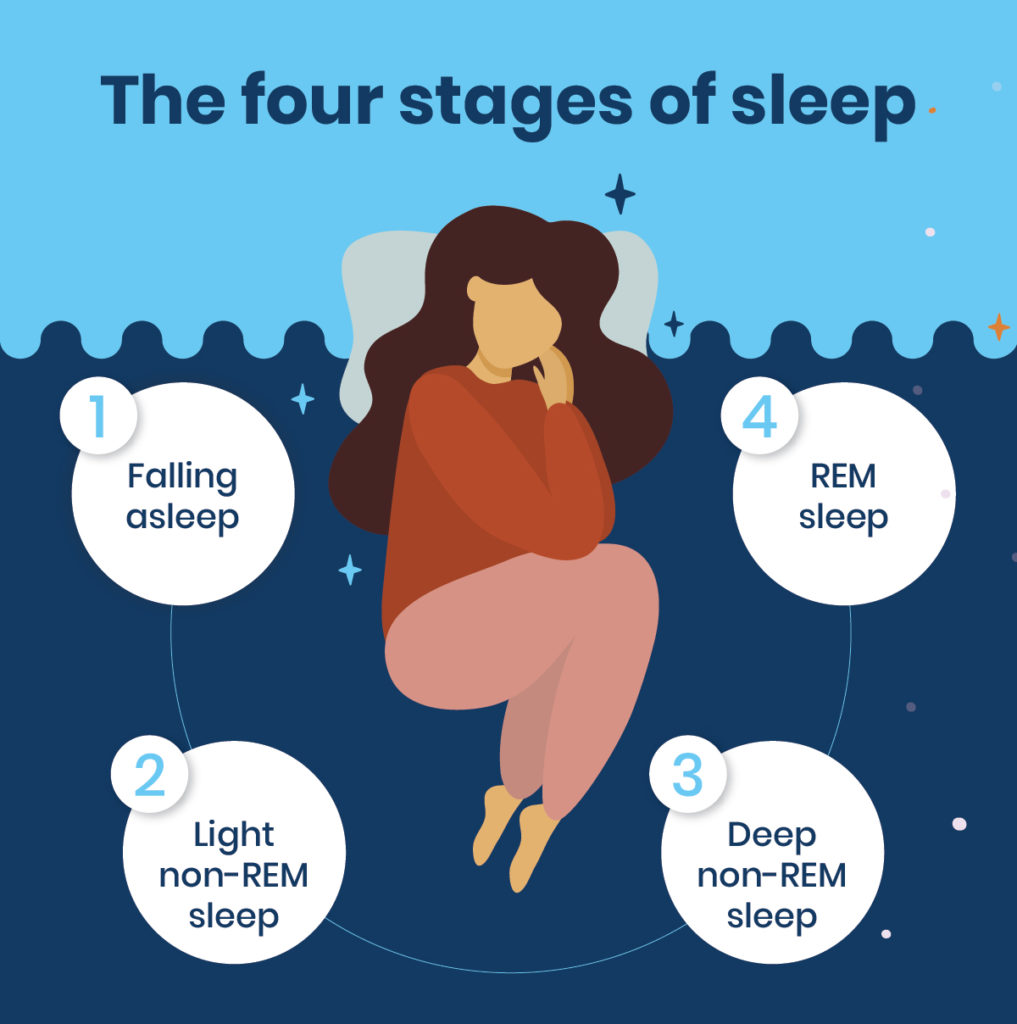
Sleep is divided into two main types: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3.
During N1 stage, which is the lightest stage of sleep, we are in the transition between being awake and asleep. Our muscles start to relax and our eyes may move slowly. This stage lasts only a few minutes.
N2 stage is a deeper stage of sleep where our body temperature drops and our heart rate slows down. This stage lasts about 20 minutes.
N3 stage is the deepest stage of sleep where our muscles are completely relaxed and our breathing slows down. This stage is also called slow-wave sleep, and it is during this stage that our body repairs and restores itself.
Finally, REM sleep is when we have vivid dreams and our eyes move rapidly. This stage is characterized by increased brain activity and increased heart rate and blood pressure.
Benefits of a good night’s sleep
Improves Physical Health
Getting enough sleep is important for our physical health. During sleep, our bodies repair and restore themselves. For example, our muscles rebuild and repair any damage, and our immune system strengthens. Additionally, sleep helps regulate our hormone levels, which is essential for maintaining good health.
Enhances Mental and Emotional Health
Sleep also has a significant impact on our mental and emotional health. Lack of sleep can lead to mood swings, irritability, and anxiety. On the other hand, getting enough sleep can improve our mood, increase our ability to focus, and enhance our overall well-being.
Promotes Weight Loss
Studies have shown that getting enough sleep can help with weight loss. Lack of sleep disrupts the hormones that regulate hunger and fullness, which can lead to overeating and weight gain. On the other hand, getting enough sleep can help regulate these hormones and promote weight loss.
Reduces the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Getting enough sleep has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. This is because sleep helps regulate our hormone levels, which can reduce the risk of these conditions.
The Effects of Sleep Deprivation
A lack of sleep can have a significant impact on our physical and mental health. When we don’t get enough sleep, our bodies are unable to repair and restore themselves, leading to fatigue and irritability. Chronic sleep deprivation can also increase our risk of serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
In addition to physical health problems, sleep deprivation can also have a significant impact on our mental health. Lack of sleep can lead to depression, anxiety, and decreased cognitive function. When we’re sleep-deprived, we’re also more likely to make mistakes and have difficulty concentrating and problem-solving.
Some of the effects of sleep deprivation include:
- Decreased Cognitive Function
Lack of sleep can impact our ability to think, concentrate, and make decisions. This can lead to decreased cognitive function and increased risk of accidents and mistakes. - Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases
Sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. - Increased Risk of Mental Health Issues
Lack of sleep can also increase the risk of mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and mood swings.
Tips for Better Sleep
Getting a good night’s sleep is essential for our overall health and well-being. Here are some tips to help you get the sweet dreams you need:
- Establish a Bedtime Routine
Establishing a bedtime routine can help improve the quality of your sleep. This can include activities like reading a book, meditating, or stretching. - Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment
Your sleep environment can also impact the quality of your sleep. Make sure your bedroom is quiet, dark, and cool. Consider investing in a comfortable mattress and pillows. You can also use black-out curtains to block out any light and minimize noise with earplugs or a white noise machine. - Limit Screen Time Before Bed
The blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with your sleep. Try to limit your use of electronic devices, such as phones and laptops, at least an hour before bedtime. If you must use your devices, consider using a blue light filter to reduce the amount of blue light you are exposed to. - Exercise Regularly
Exercising regularly can help improve the quality of your sleep. However, avoid strenuous exercise close to bedtime as this can make it more difficult to fall asleep. - Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol
Caffeine and alcohol can interfere with your sleep. Try to avoid consuming these substances at least 4-6 hours before bedtime. - Practice Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and improve the quality of your sleep.
In conclusion, getting enough sleep is essential for our physical, mental, and emotional health. By following these tips and establishing good sleep habits, you can improve the quality of your sleep and experience the many benefits that come with a good night’s sleep. Remember, sweet dreams lead to sweet days!
Visit us at Wilmington 1st Walk-In if you need help and advice.
