10 foods that improve gut health. When people refer to “gut” in the context of human physiology, they are usually referring to the gastrointestinal tract, which is a series of organs involved in the process of digestion and nutrient absorption.
The gut, also known as the digestive tract, starts at the mouth and extends to the anus. It includes organs such as the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum, and anus. The gut plays a crucial role in breaking down food, extracting nutrients, and eliminating waste products from the body.
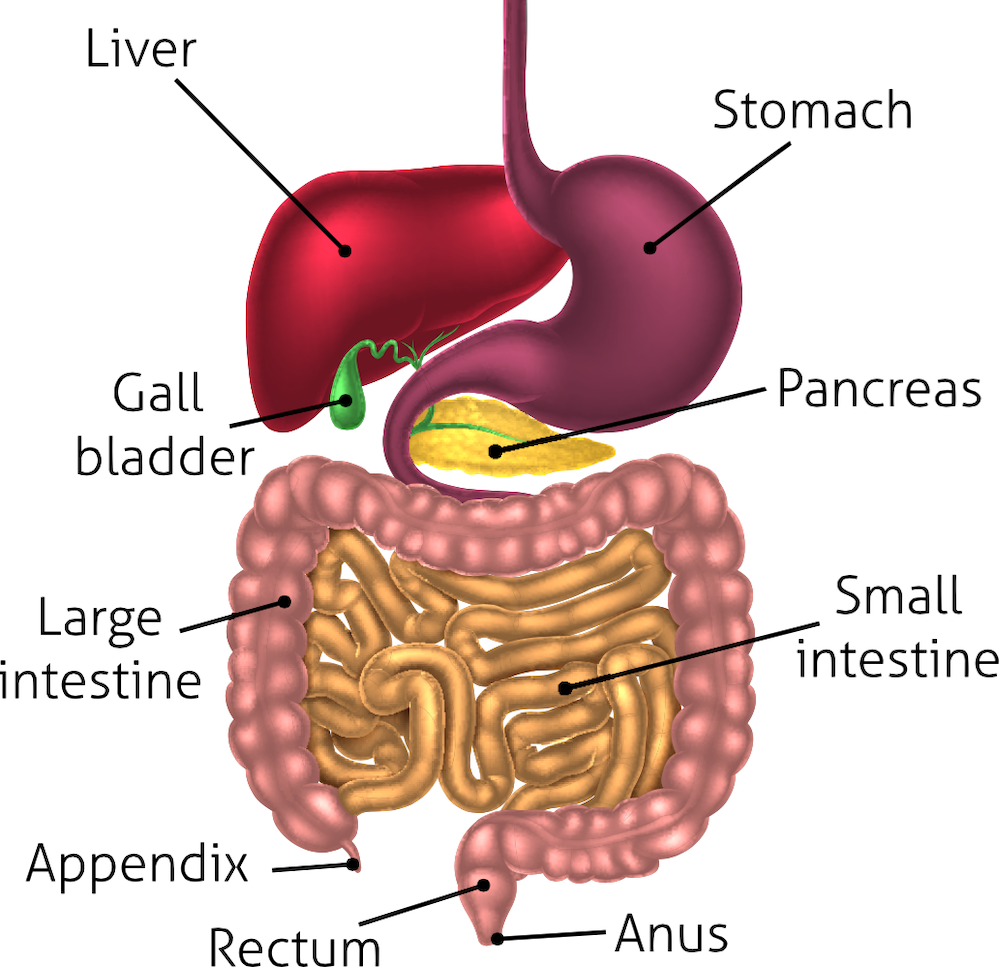
The gut is not only responsible for processing food but also plays a critical role in various aspects of well-being, including immune system regulation, hormone production, and even mental health. The balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria in the gut is crucial for maintaining optimal gut health and overall well-being.
Why is gut health important?
see the link between gut and brain here.
Gut health is important for several reasons, as it affects various aspects of overall well-being. Here are some key reasons why gut health is crucial:
- Digestion and Nutrient Absorption: The gut is responsible for breaking down food into smaller components and absorbing nutrients into the bloodstream. A healthy gut ensures efficient digestion and optimal absorption of nutrients, vitamins, and minerals, which are essential for proper bodily functions.
- Gut Microbiota and Immune Function: The gut is home to a diverse community of microorganisms known as the gut microbiota. A balanced and diverse gut microbiota is important for a well-functioning immune system. Beneficial gut bacteria help regulate immune responses, defend against harmful pathogens, and promote immune tolerance. An imbalance in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infections and autoimmune conditions.
- Mental Health and Brain Function: The gut and brain are connected through the gut-brain axis, which involves bidirectional communication between the two. The gut produces neurotransmitters and hormones that can influence mood, emotions, and cognitive function. Research suggests that an unhealthy gut may contribute to mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and even neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
- Inflammation and Chronic Diseases: A healthy gut helps maintain a balanced immune response, preventing chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation in the gut can lead to the development of various diseases, including inflammatory bowel diseases (such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis), obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers. Promoting gut health can reduce the risk of these chronic conditions.
- Digestive Disorders and Symptoms: A well-functioning gut is less prone to digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, diarrhea, and bloating. By maintaining a healthy gut, one can improve digestion, alleviate gastrointestinal discomfort, and promote regular bowel movements.
- Absorption of Medications: The gut plays a crucial role in the absorption of orally administered medications. An unhealthy gut can impact the absorption and effectiveness of certain medications. Maintaining gut health can enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of medications.
To support gut health, it is recommended to consume a balanced diet rich in fiber, whole foods, and probiotics, manage stress levels, stay hydrated, exercise regularly, and avoid excessive consumption of processed foods, sugar, and alcohol. It’s worth noting that individual needs may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for improving gut health.
10 foods that improve gut health

Here’s are ten foods that can improve gut health:
- Yogurt: Yogurt is a fermented dairy product that is rich in beneficial bacteria known as probiotics. These live bacteria help restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut microbiota. Probiotics in yogurt, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, can improve digestion, support immune function, and reduce inflammation in the gut.
- Kimchi: Kimchi is a popular Korean dish made by fermenting vegetables, mainly cabbage, with a variety of seasonings. The fermentation process produces probiotics that enhance gut health. Kimchi is rich in vitamins A, B, and C, as well as fiber. It can help improve digestion, boost the immune system, and reduce the risk of certain digestive disorders.
- Kefir: Kefir is a fermented beverage, typically made from cow’s milk or plant-based milk alternatives, such as coconut milk or almond milk. It is loaded with probiotics and provides a diverse range of beneficial bacteria and yeast strains. Kefir helps restore gut flora, supports digestion, and may alleviate symptoms of lactose intolerance.
- Sauerkraut: Sauerkraut is a fermented food made by fermenting cabbage with salt. During fermentation, the cabbage undergoes lactic acid fermentation, resulting in the growth of beneficial bacteria. Sauerkraut is an excellent source of probiotics, fiber, vitamins C and K, and antioxidants. Regular consumption of sauerkraut can improve gut health, enhance digestion, and support immune function.
- Garlic: Garlic is not only a flavorful culinary ingredient but also a valuable ally for gut health. It contains compounds like allicin, which have antimicrobial properties that help combat harmful bacteria in the gut. Additionally, garlic contains prebiotics, which serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, stimulating their growth and promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
- Ginger: Ginger has been used for centuries to alleviate digestive issues and promote overall gut health. It possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce gastrointestinal irritation and inflammation. Ginger stimulates the production of digestive enzymes, aids in nutrient absorption, and can relieve symptoms of indigestion, bloating, and nausea.
- Blueberries: Blueberries are a rich source of antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which have anti-inflammatory properties. The fiber content in blueberries promotes regular bowel movements and helps feed the beneficial bacteria in the gut. By reducing inflammation and supporting a healthy gut environment, blueberries contribute to improved digestive health.
- Almonds: Almonds are a nutritious nut that provides a combination of healthy fats, fiber, and protein. The fiber in almonds acts as a prebiotic, nourishing the beneficial bacteria in the gut. This promotes a diverse and thriving gut microbiome. Almonds can help improve digestive regularity and may contribute to reduced inflammation in the gut.
- Lentils: Lentils are legumes that are high in fiber, protein, and various vitamins and minerals. The fiber in lentils acts as a prebiotic, supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Consuming lentils can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, regulate bowel movements, and contribute to better overall digestive health.
- Dark chocolate: Dark chocolate with a cocoa content of 70% or higher contains prebiotic fibers, such as inulin and polyphenols, that can serve as nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. These prebiotics support the growth and activity of probiotics in the gut. Consuming small amounts of dark chocolate can have a positive impact on gut health while providing antioxidants and potential mood-boosting benefits.
Incorporating these foods into a balanced diet can help improve gut health, enhance digestion, support immune function, and reduce inflammation in the gut. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs and health goals.

One comment
Pingback: How to Manage High Blood Pressure - Wilmington 1st Walk-In
Comments are closed.